- Overview
- Features
- Technical Details
- Application
- Download
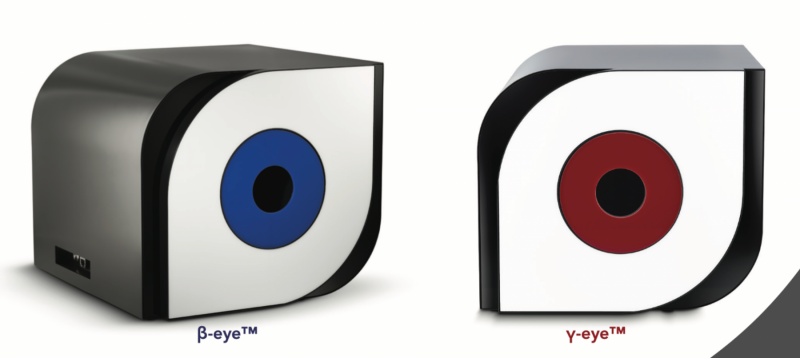
Eyes:
Novel, desktop imaging tools for in-vivo mouse radioisotopic screening
• Unique benchtop systems for in-vivo imaging of radiolabeled biomolecules and nanoparticles.
• Filling the gap between ex-vivo biodistributions and advanced imaging systems.
• The eyes have a 5x10 cm2 field of view, allowing whole-body mice imaging studies.
• Both systems support static and fast dynamic whole-body mice imaging studies.
• The β-eye allows for the imaging of biomolecules labelled with PET isotopes.
• The γ-eye allows for the imaging of biomolecules labelled with SPECT isotopes.
• The systems operate in planar mode, the most efficient method for fast, in vivo screening.
• Complete with a durable packing suitcase and all components ready for immediate use.
• The only truly portable molecular imaging systems in the market!

- Smallest footprint in the market – Truly desktop
- Real-time dynamic Imaging during acquisition
- Suitable for Radio-TLC and organ ex-vivo imaging
- Cost in the range of lab-equipment
- ~1.5mm spatial resolution for all PET isotopes
- Down to 5 sec frames for whole body scans
- Low activities 1MBq can be easily imaged
- 90% quantitative accuracy compared to 3D systems
- Time activity curves ready at the end of the acquisition
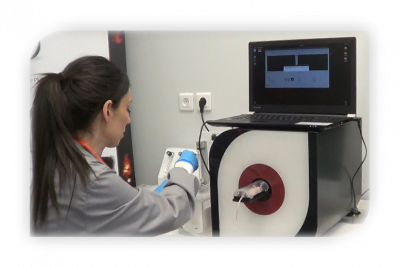
Complete Solution
- Animal bed supporting heating and anesthesia
- Includes laptop with pre-installed acquisition and analysis software
- Export in DICOM files and database
- Delivered in a protective, easily transportable suitcase
- Can be shipped directly to client’s site
- Smallest footprint in the market – Truly desktop
- Real-time dynamic Imaging during acquisition
- Suitable for Radio-TLC and organ ex-vivo imaging
- Cost in the range of lab-equipment
- <2mm spatial resolution for Tc99m, In111, Lu177
- Down to 10 sec frames for whole body scans
- Low activities <1MBq can be easily imaged
- 95% quantitative accuracy compared to 3D systems
- Time activity curves ready at the end of the acquisition
Complete Solution
- Animal bed supporting heating and anesthesia
- Includes laptop with pre-installed acquisition and analysis software
- Export in DICOM files and database
- Delivered in a protective, easily transportable suitcase
- Can be shipped directly to client’s site


If you work with ex vivo biodistributions, using the eyes you can:
- Obtain full dataset non-invasively, for each animal
-
Minimize the number of required animals per study
-
Significantly improve statistics and accuracy
-
Reduce cost and time for testing candidate products
-
Evaluate small variations in synthesis in vivo
-
Test different injection routes easily and fast
-
Study the effect of anesthesia protocols in a few animals
-
Assess animal preparation conditions non-invasively
-
Test and optimize different injected concentrations
-
Identify bad injections or unexpected behavior
-
Obtain a quality assurance tool for planning biodistributions
-
Comply with bioethical standards and the 3Rs Principle
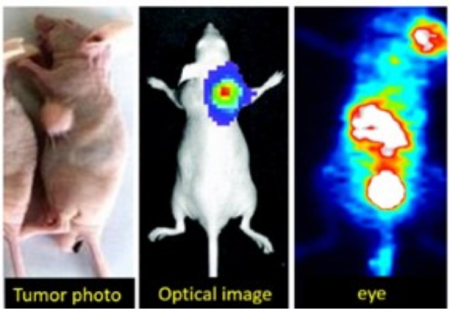
If you work in tumor research planar with optical imaging, using the eyes can:
13. Provide images of high resolution with no penetration depth
14. Offer quantitative data for subcutaneous tumors
15. Allow pharmacokinetic analysis in major organs
16. Allow direct translation for follow up research on larger animals
17. Offer a much lower cost compared to optical imaging
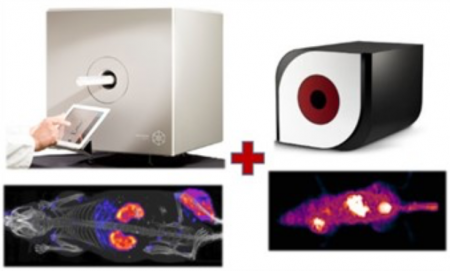
If you work with multimodal systems, the eyes enable you to fully exploit them:
18. Have a screening tool for daily use in your lab
19. Optimize protocol parameters before 3D imaging
20. Define the optimal time points for 3D imaging
21. Select the best animal for 3D imaging
22. Avoid imaging animals with bad biodistribution
23. Check successful injection before 3D scan
24. Save resources when “buying” imaging time

And what surprisingly most tomographic systems do not offer, but the eyes do:
25. Continuous whole body mouse images, right from the first second post injection
26. Acquire short frames, down to 10sec for fast dynamic studies
27. Ability to image low activities, even below 10uCi
28. Image first blood pass by injecting the mouse on the camera
29. Provide animal anesthesia, with all cables inside the system
30. Possibility to image many organs ex vivo, as an alternative to biodistribution